树与二叉树的深度优先与广度优先算法(递归与非递归)
9,769 views
0
本博客前面文章已对树与二叉树有过简单的介绍,本文主要是重点介绍有关二叉树的一些具体操作与应用
阅读本文前,可以先参考本博客
各种基本算法实现小结(三)—— 树与二叉树
和
各种基本算法实现小结(二)—— 堆 栈
二叉树
深度层数、叶子数、节点数和广度优先算法
以及树的先序、中序、后序的递归与非递归(深度优先)
测试环境:VS2008(C)
运行结果:
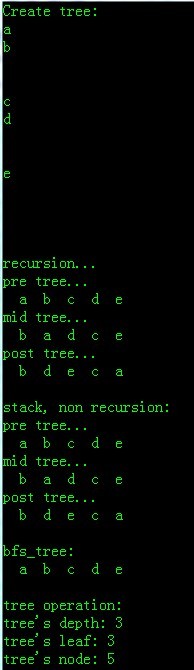

======================================
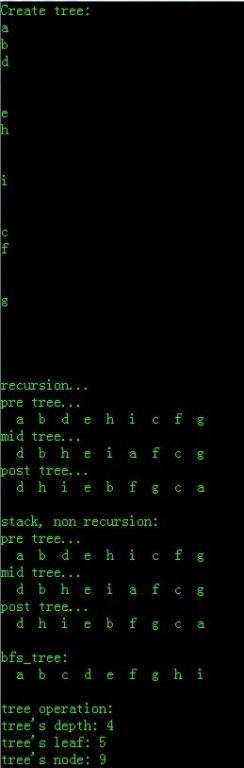

===================================================================
版权所有: 本文系米扑博客原创、转载、摘录,或修订后发表,最后更新于 2010-06-22 16:12:52
侵权处理: 本个人博客,不盈利,若侵犯了您的作品权,请联系博主删除,莫恶意,索钱财,感谢!